Streptococcus pneumoniae is called the pneumococcus!
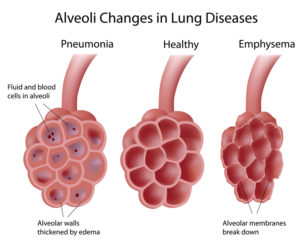
Streptococcus pneumoniae, which is also called the pneumococcus, is a bacterium that is commonly found in the upper respiratory tract of human beings. It can sometimes infect the lung, resulting in pneumonia. In cases of pneumonia, the air sacs in the lung fill with fluid.
The infection can sometimes spread throughout the body via the bloodstream (sepsis). An infection that reaches the fluid surrounding the brain is called meningitis because it causes inflammation of the meninges, which are the membranes that cover the brain. Bacterial meningitis is a serious disease.
The pneumococcus bacterium is surrounded by a capsule made out of complicated sugars (polysaccharides). Different strains of pneumococcus have different polysaccharides in their capsule. The older vaccines against pneumococci were made out of these polysaccharides. The newer vaccines are conjugate vaccines, which means that the polysaccharide is bound to a bit of protein. This protein helps the immune system develop a stronger immune response to the pneumococcus. As this video explains, the use of the conjugate vaccine has decreased the number of children with bloodstream or meningitis due to pneumococcal infection.